| Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts Guide | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts Guide | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
Oracle Enterprise Manager is the cornerstone of the strategy which makes Oracle the most manageable database for the enterprise. The Oracle Enterprise Manager product family consists of next generation system management tools designed to efficiently manage the complete Oracle environment.
As you migrate from large centralized mainframe systems to smaller distributed systems, the task of being a database administrator (DBA) becomes increasingly difficult. As an Oracle DBA you are often responsible for managing a highly divergent combination of local and remote systems. In this environment, you require easy-to-use and effective tools that administer distributed systems from a single site.
Oracle Enterprise Manager provides Oracle database administrators with an intuitive, easy-to-use interface and a high degree of automation through remote task execution and reactive and proactive management capabilities. It also scales to accommodate both very large database configurations, while being flexible enough to handle installations with very many databases. Oracle Enterprise Manager includes an open-architecture design, providing third-party vendors and customers with the ability to integrate their applications into Oracle Corporation's system management platform.
From the Enterprise Manager Console, you can
The Oracle Enterprise Manager uses Transparent Network Substrate (TNS) and SQL*Net which permit a heterogeneous system (one with multiple protocols) to be managed as easily as a homogeneous one. You can schedule jobs on multiple nodes simultaneously or easily monitor groups of services together.
Oracle Enterprise Manager is optimized for very many database scenarios through caching and multi-threaded processing.
The Job Scheduling system provides you with the ability to automate routine tasks. You can schedule tasks such as database backups or running reports on a regular basis, thereby freeing your time to focus on value-added tasks. The Job Scheduling System can schedule and run jobs on remote sites, providing the kind of "lights out" management that is vital in a large, distributed environment.
Using the Oracle Enterprise Manager's Event Management system, you can remotely monitor for critical database and system events. You define which events are of interest, and when one of these events is detected, it is represented graphically on the Console. In addition, you can choose to be notified through electronic mail or page.
To further automate problem detection and correction, you can specify for Oracle Enterprise Manager to perform tasks in response to an event. For example, you can register an event to monitor the space usage of a tablespace and, if necessary, run a fix-it job to allocate a new datafile to the tablespace.
This ability of proactive management of an event allows you to ensure that a problem is corrected before it noticeably impacts end-users.
Note:
Intelligent Autonomous Agent
You can localize task execution, so that DBA tasks are completed even when a crucial part of the network is down. Localized tasks are reliable because all job processing is done by the agent. For example, if you schedule a job on a node, it will be executed locally at the specified time. In addition, because the job is executed locally, it will run even if a network outage occurs between the node and the Console. Easy-to-Use Security
Oracle Manager's Security System provides easy-to-use administrator level security, allowing the administrator single sign-on access to particular databases. The Basic Components
This section describes the following components of Oracle Enterprise Manager
The windows provide you with a tree list (a hierarchical view of Oracle services on the network) and a topographical or map view (which permits Oracle services to be grouped based on spatial relationships, function, or both). The map view shows the network and connects to the Job Scheduling and Event Management Systems.
The menus, toolbars, and palettes allow you to perform DBA tasks, such as submitting a job or creating a user.
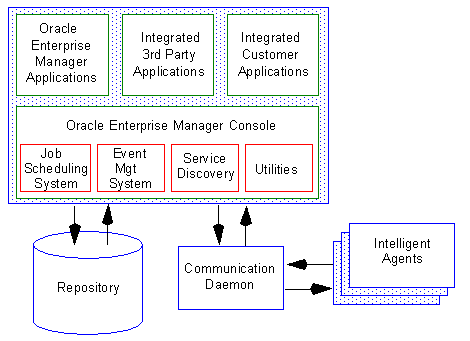
Figure 1-1: Enterprise Manager Architecture
Job Scheduling System
With the Job Scheduling System, you can schedule and run jobs on remote sites throughout the network. Event Management System
You can monitor specific events at remote sites throughout the network. To automate problem detection and correction, you can also specify a fixit job to be run in response to a particular event. Repository
The Enterprise Manager repository is a database which is accessible from the console. The repository
The repository provides a centralized location for storing information about the state of the environment managed by Oracle Enterprise Manager from the perspective of each console user. It contains information on configurations, jobs and events, historical collections, tuning recommendations, the preferred credentials for each user, and other information associated with each Enterprise Manager Console login.
The Intelligent Agent is a process that runs on remote nodes. It is both effective and non-intrusive, and functions as the executor of jobs and events sent by the console via the communication daemon. High availability is ensured since the agent can function regardless of the status of the Console or network connections.
The communication daemon is a process that runs on the client Console machine. The daemon communicates with an agent to manage jobs and events.
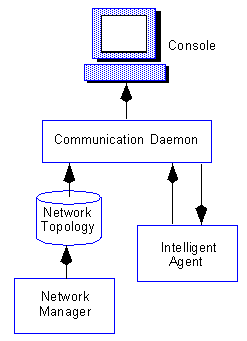
Figure 1-2: Service Discovery
Security
Access to Oracle Services on the network is controlled by a set of user-defined, preferred credentials for the available nodes and services. Enterprise Manager caches the user authentication information in encrypted form in the repository and provides it as part of the connection request from the Enterprise Manager console or console launched applications. Integrated Applications
Oracle Enterprise Manager includes a set of standard integrated database administration (DBA) applications. These applications are specialized management tools that can be launched directly from the Console or the Administration Toolbar. Because Enterprise Manager has an open architecture, third-parties can also write applications that integrate into the Console and use the available common services. These applications can be launched directly from the Console.
|
Prev Next |
Copyright © 1996 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |